USD
/
USD
/
Shipping to:
Currency:
What Is the Difference Between Andalusite and Axinite?
When it comes to the fascinating world of gemstones, understanding the nuances between similar-looking minerals can be both intriguing and essential, especially for collectors and enthusiasts. Two such gemstones that often invite comparison are andalusite and axinite. While they may share some visual similarities, they are distinct in their properties, origins, and uses. Let’s delve into the characteristics that set these two apart.
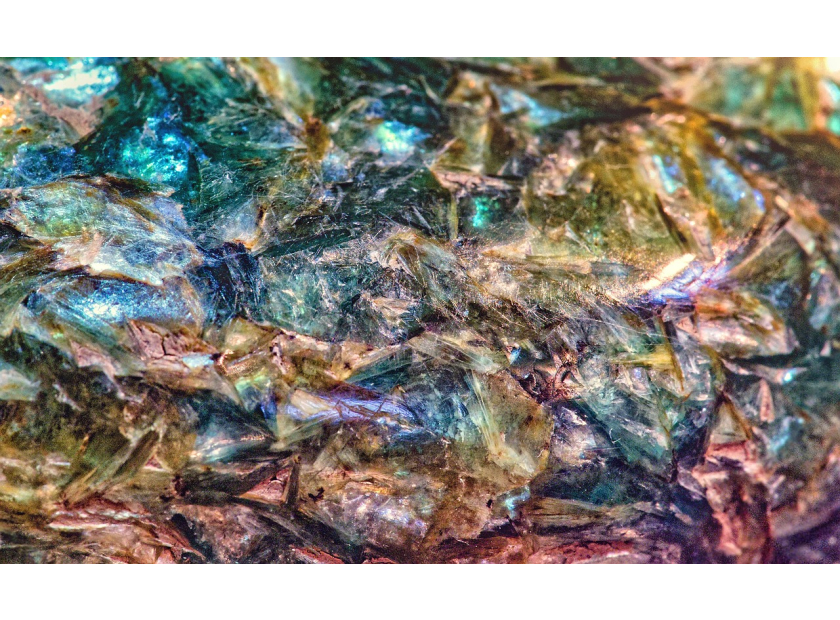
Andalusite: A Gem of Many Colors
Andalusite is renowned for its remarkable pleochroism, meaning it can display multiple colors when viewed from different angles. Typically, this gemstone exhibits shades of green, brown, and reddish hues, creating a captivating visual effect. This unique characteristic makes andalusite particularly appealing for jewelry, as it offers a dynamic range of colors within a single stone. If you’re looking to explore a range of stunning gemstones, check out our gemstone selection.
Axinite: The Collector’s Rarity
Axinite, on the other hand, is a rare gemstone primarily known among collectors. It typically presents in hues of brown, violet, and sometimes gray. Like andalusite, axinite also exhibits pleochroism, though its color range and intensity differ. Due to its rarity and unique crystal formations, axinite is less commonly used in mainstream jewelry but holds significant value for mineral enthusiasts. If you’re intrigued by gemstones and their rarity, you might also want to check out how gemstones and diamonds are formed.
Distinguishing Between Andalusite and Axinite
While both gemstones display pleochroism, there are key differences:
- Color Palette: Andalusite often shows a mix of green and reddish-brown tones, whereas axinite leans towards brown and violet shades.
- Crystal Structure: Andalusite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system, giving it a distinct crystal habit, while axinite forms in the triclinic system, often resulting in wedge-shaped crystals.
- Hardness: Andalusite has a hardness of about 7.5 on the Mohs scale, making it suitable for various types of jewelry. Axinite is slightly softer, with a hardness ranging from 6 to 7, which may require more careful handling.
- Occurrence and Rarity: Andalusite is found in several locations worldwide, including Spain and Sri Lanka, and is relatively more accessible. Axinite is rarer, with notable sources in France and the USA, making it less commonly encountered in the gem market. If you're in search of beautiful engagement rings with a variety of gemstones, you might want to check out our gemstone engagement rings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can andalusite and axinite be easily confused?
While they share some visual similarities, their distinct color ranges, crystal structures, and hardness levels usually allow for differentiation, especially with proper gemological equipment.
Which gemstone is more suitable for everyday jewelry?
Andalusite, with its higher hardness and vibrant pleochroic colors, is generally more suitable for regular wear in various jewelry settings. For more jewelry options, explore our non-traditional engagement rings.
Are synthetic versions of these gemstones common?
Synthetic andalusite and axinite are not commonly found in the market, as their natural forms are preferred and valued for their unique properties.