GBP
/
GBP
/
Shipping to:
Currency:
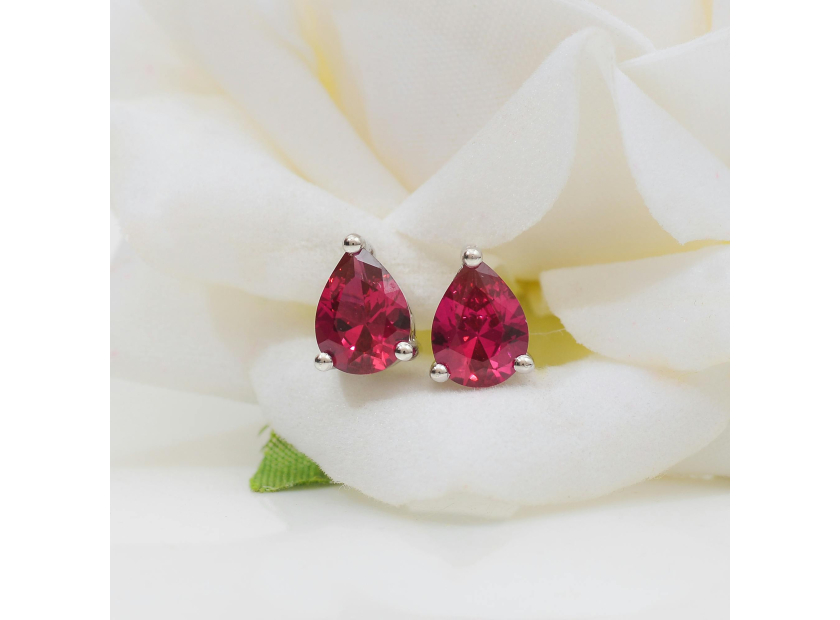
Rubies have long been cherished for their deep, captivating red hues and remarkable durability.
As one of the most sought-after gemstones, they often command high prices, making them prime targets for imitation and synthetic alternatives.
Whether you're considering a purchase or simply curious about a ruby you already own, it's essential to know how to distinguish a genuine ruby from a counterfeit.
This guide will walk you through various methods to help you identify a real ruby, from simple visual inspections to more advanced testing techniques.
Importance of Identifying Genuine Rubies
Determining the authenticity of a ruby is crucial for several reasons:
- Value Assessment: Natural rubies are significantly more valuable than their synthetic or imitation counterparts.
- Investment Protection: Ensuring you're purchasing a genuine ruby safeguards your financial investment.
- Sentimental Significance: Authentic rubies often carry historical or familial importance, making their authenticity vital.
If you're shopping for alternatives, you may also want to check out gemstone engagement rings which feature ethically sourced, natural gemstones.
Understanding Rubies
Rubies are a variety of the mineral corundum, characterised by their red colour, which results from the presence of chromium.
While sapphires are also forms of corundum, they encompass all other colours except red.
The most prized rubies exhibit a deep, vivid red, often referred to as "pigeon's blood" red.
For a deeper look at gemstone formation and how rubies compare to diamonds, check out this guide on how and where gemstones and diamonds are formed.
Visual Inspection Techniques
Evaluating Colour and Clarity
A genuine ruby typically showcases a rich, vibrant red hue.
However, natural rubies often contain inclusions—tiny internal flaws—which can affect their clarity.
Be cautious of stones that appear overly clear or have a colour that seems too perfect, as these may be synthetic.
It's worth noting that some natural rubies can also exhibit exceptional clarity, but these are rare and usually come with certification.
If you're unsure whether to choose natural or lab-created stones, check out this comparison on lab-grown diamonds vs gemstones.
Checking for Inclusions
Natural rubies usually have small inclusions, such as tiny crystals or needle-like structures known as "silk."
These inclusions are formed naturally during the gemstone's creation and are often unique to each stone.
In contrast, synthetic rubies may contain gas bubbles or display curved growth lines, which are not typically found in natural rubies.
Assessing Hardness
Rubies score a 9 on the Mohs scale of hardness, making them exceptionally hard.
This means they can scratch most other materials but should not be easily scratched themselves.
However, conducting a scratch test at home is not recommended, as it can damage the stone or its setting.
Advanced Testing Methods
Using a Loupe or Microscope
Examining a ruby under magnification can reveal internal characteristics indicative of its origin.
Natural rubies may display inclusions like rutile needles, while synthetic ones might show curved striae or gas bubbles.
A jeweller's loupe or microscope can aid in this inspection.
If you’re exploring other striking and ethical stone options, you may want to check out these non-traditional engagement rings featuring unique gemstones.
Conducting a UV Light Test
Both natural and synthetic rubies can fluoresce under ultraviolet (UV) light, typically emitting a red or pink glow.
However, the intensity and nature of this fluorescence can vary.
Some synthetic rubies may exhibit a more intense fluorescence compared to natural ones.
It's important to note that not all rubies will fluoresce, and the absence of fluorescence doesn't necessarily indicate a fake.
Heat Conductivity Testing
While diamond testers measure heat conductivity to identify diamonds, they are not reliable for testing rubies.
Rubies and their imitations can have similar thermal properties, making this method inconclusive.
Importance of Professional Certification
For high-value rubies, obtaining a certificate from a reputable gemological laboratory, such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the International Gemological Institute (IGI), is advisable.
These certificates provide an expert assessment of the ruby's authenticity and quality.
You can also explore certified, authentic gemstone jewellery in the gemstone rings collection.
Common Ruby Imitations
Red Spinel
Historically mistaken for rubies, red spinels can closely resemble them but have different chemical compositions.
Unlike rubies, spinels have a different crystal structure and lack the same hardness.
Garnet
Red garnets can mimic the appearance of rubies but typically have a deeper red with brownish undertones.
They are also softer than rubies and have different refractive properties.
Glass Imitations
Some fake rubies are merely coloured glass.
These can often be identified by the presence of bubbles within the stone and a lack of hardness compared to genuine rubies.
If you're considering ruby alternatives, you might also like to browse these diamond wedding rings for timeless sparkle.
Tips for Purchasing a Genuine Ruby
- Buy from Reputable Dealers: Ensure the seller has a solid reputation and positive reviews.
- Request Certification: Ask for a gemological certificate from a recognised laboratory.
- Be Cautious of Deals That Seem Too Good to Be True: High-quality rubies are rare and expensive; unusually low prices may indicate a fake.
- Consider Alternative Gemstones: If you're open to other options, explore gemstone engagement rings for a unique and vibrant choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I determine if a ruby is real just by looking at it?
While certain visual cues can provide hints, accurately determining a ruby's authenticity typically requires professional evaluation.
Natural and synthetic rubies can appear very similar to the untrained eye.
Do all real rubies have inclusions?
Most natural rubies contain inclusions, but the absence of visible inclusions doesn't necessarily mean a ruby is synthetic.
Some high-quality natural rubies have exceptional clarity.
Is a ruby that glows under UV light always real?
Not necessarily.
Both natural and synthetic rubies can fluoresce under UV light.
The nature of the fluorescence can vary, so this test alone isn't conclusive.